Hvac Systems

HVAC SYSTEMS
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) is a collective term used to describe the various components that control your home’s indoor temperature, helping to ensure your family’s comfort year-round. According to Consumer Reports, over 50% of your home’s energy usage goes towards heating and cooling
Regulating your home’s temperature eliminates the need to run an air conditioner or heater when not necessary. The system also functions to regulate humidity levels and to filter out dust, pollen, dander and other allergen particles to improve air quality. Poor air quality can not only have a negative impact on your productivity, it can also have a significant effect on your family’s overall health and well-being.

How Do HVAC Systems Work?
In short, a quality HVAC system will cool rooms by moving warm air outside, and warm rooms by moving warm air inside. Since an HVAC system maintains consistent temperatures, you can be certain that your home is always comfortable.
Having a basic understanding of how an HVAC system works will help you be better prepared to properly maintain it. In general, there are two categories of HVAC systems:
Ducted
Requires a system of ducts (located inside walls and ceilings) that distribute air throughout a home. Duct systems consist of a central unit which treats the air, and a blower that circulates the treated air through the ductwork and into your home. The ducts need to be maintained regularly to ensure there are no blockages and that there is no accumulation of debris etc.
- Example: Central Air Conditioning
Ductless
Ductless systems distribute warm or cool air without requiring ductwork. Instead of air flowing through ducts, air is exchanged directly into the living space.
- Example: Mini-Split System
Heating
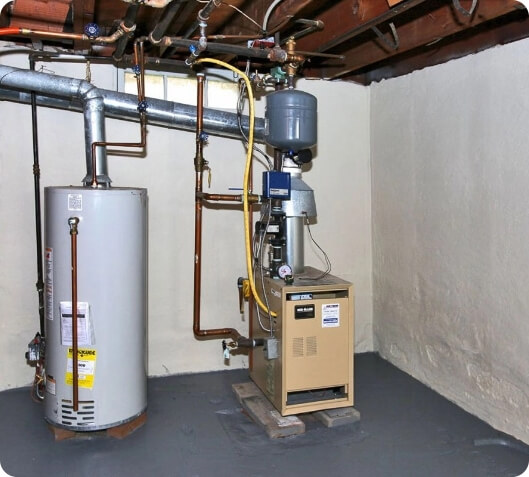

Boilers
Unlike a furnace, which uses fuel to heat air, a boiler contains water to create heat. The boiler converts the water into steam. The steam is then distributed to a network of radiators throughout the home which circulates heat to each room. As the steam or water cools, it returns to the boiler for reheating.
Boilers are typically run on heating oil or natural gas and can also be combined with a water heater for added energy efficiency. While modern boiler systems include hefty safety features, if not properly maintained, a boiler system can be very dangerous.
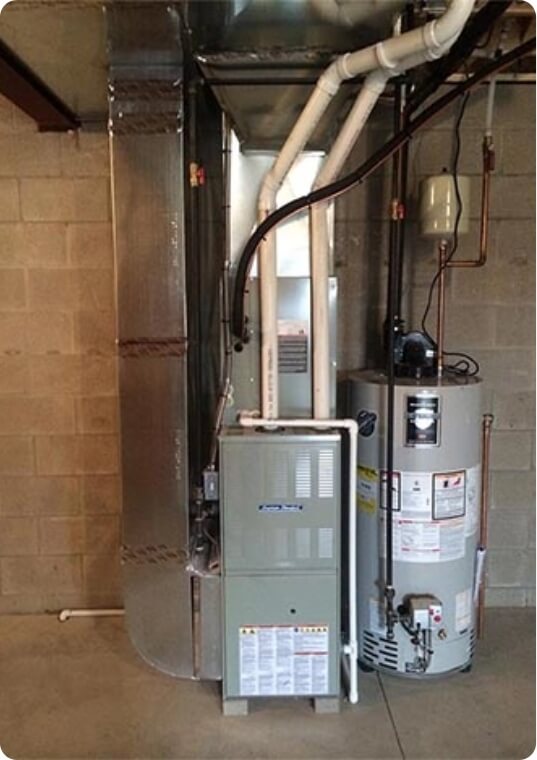

Furnaces
Furnaces use electricity to burn fuel (such as natural gas, heating oil or liquid propane) in order to create heat. All furnaces consist of four components:
Burner (burns and delivers fuel)
Heat exchangers
Blower
Flue (acts to expel dangerous gasses)
Most modern furnaces are forced-air systems, where heated air is circulated by a blower/fan through a home’s ducts. In order to keep the furnace functioning properly, a filter traps dust and other debris, helping to purify the air.
It’s recommended that your furnace should be replaced if it is over 15 years old.
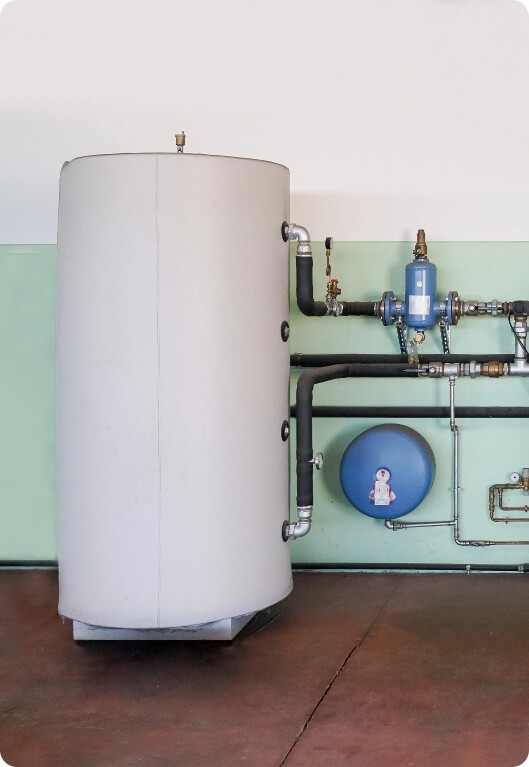

Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are often misunderstood because the name implies they only distribute heat. Believe it or not, heat pumps actually provide both heating and cooling. Similar to an air conditioning unit, a heat pump uses refrigerant to transfer heat outside in order to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. In cooler weather, the heat pump allows heat from outdoor air (or the ground if it is a geothermal heat pump) to flow inside and circulate warm air.
Heat pumps can provide heating and cooling via ductwork or ductless units which look and function like a mini-split. In addition, because they don’t require fuel to operate, heat pumps are more eco-friendly than other heating solutions and won’t produce dangerous gas, such as carbon monoxide. According to the U.S. Department of Energy heat pumps use 50% less electricity to produce as much heat as a furnace or baseboard heater.
It’s recommended that your heat pump should be replaced if it is over 10 years old.

Radiant Heating (Hydronic Systems)
Radiant heating systems use hot water or steam from a boiler or electric heat cables to produce heat. The system directly heats a home’s walls or floors without the need to circulate air.
Ventilation
Ventilation is actually the most important component of an HVAC system. Improper ventilation can lead to stale air, growth of mold/mildew, foul smells and health problems. An air exchanger is a critical component of an HVAC system’s ventilation portion because it “exchanges” stale air for fresh air.
Most modern HVAC units are connected to a system of ducts to circulate air throughout the home. Ventilation ensures the air inside your home is always as clean and fresh as possible. As a result, it can also reduce dangerous allergens and control humidity levels. This is especially beneficial if someone in your family suffers from allergies, asthma or a respiratory illness.
Air Conditioning
One of the most common misperceptions is that an air conditioner cools the air. However, it actually functions to remove heat and humidity from the air.
Air conditioners help keep indoor temperatures cooler in warmer months via a liquid refrigerant that expels heat. As the refrigerant flows through the air handler inside the unit, it turns into gas. The gas then flows to a condenser which releases heat into the air outside. A compressor then turns the refrigerant back into a liquid, and the process is repeated.
The refrigerant helps remove moisture in the air, which turns into condensation. The condensation builds up on the evaporator coils and becomes water droplets. The droplets are captured by a drip pan, and are expelled via an external drain. As air is pushed through the system, it passes through air filters which remove pollen, dust and other potentially harmful allergens.
It’s recommended that your air conditioning system should be replaced if it is over 10 years old.
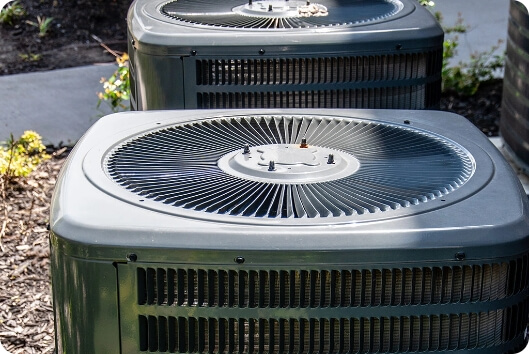
Central Air Conditioning (Split Systems)
Central air conditioning systems are controlled by a thermostat and are connected to a system of ducts that circulate cool air throughout a home. When the internal temperature rises above a specified temperature, the system will automatically turn on and will automatically turn off once the air is cooled.
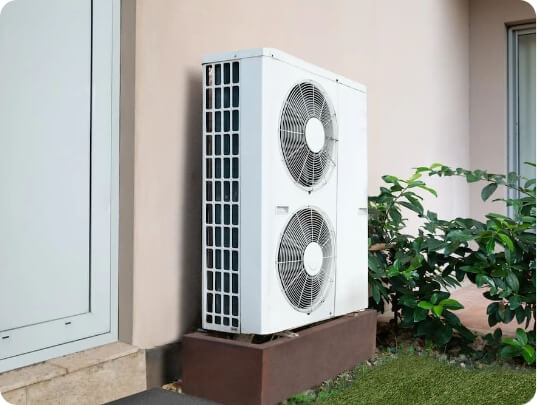

Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Mini-splits are ductless systems installed on a wall or recessed in a ceiling that cool air in one or more rooms. Like central air conditioning, a ductless mini-split system requires an outdoor condenser unit and one or more indoor air handlers. Because no ducts are required, ductless mini-split systems don’t require opening up walls, ceilings or floors to install a network of air ducts and can be installed in virtually any space.

Portable Air Conditioning Units
Portable air conditioning units connect to a window by a large tube that can be removed and packed away when not in use. Portable air conditioning units contain both an air handler which faces inside to distribute cool air, and a condenser which faces outside so the heat can be vented outside.
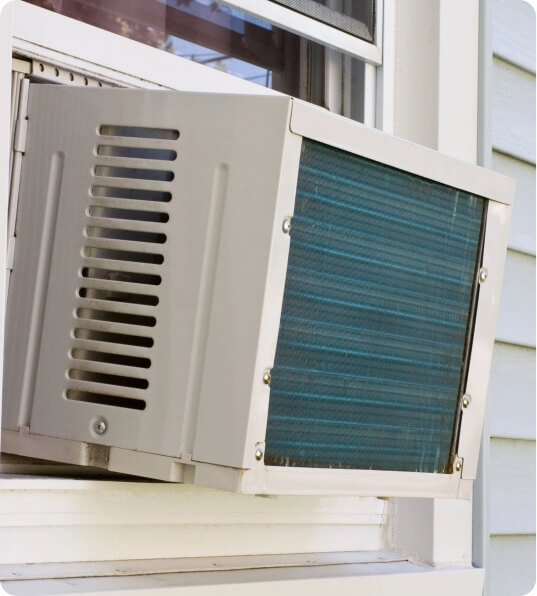

Window Air Conditioning Units
As the name suggests, window air conditioning units are installed to sit in a window. As cool air flows inside, warm air is vented outside. The unit contains an air handler which faces inside to distribute cool air, and a condenser which faces outside so the heat can be vented outside
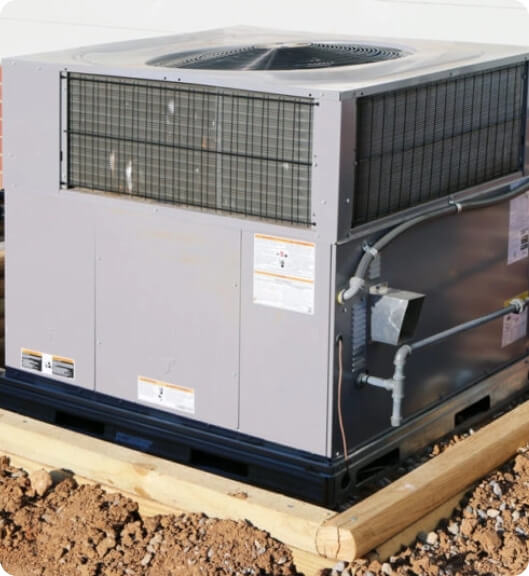

Packaged HVAC Systems
As the name implies, a packaged HVAC system combines both heating and cooling equipment. Examples of packaged HVAC systems include:
An air conditioner with added heat strips for heating.
A heat pump with extra evaporator coils for cooling.
While packaged HVAC systems are located outside the home, they are generally not as efficient as other HVAC systems, which makes packaged systems a good option for smaller sized homes.
Benefits Of An HVAC System
Today’s homeowners have many options when it comes to a home’s HVAC system. Regardless of where you live or the size of your home, investing in a quality HVAC system can produce significant benefits.

Air Quality
Without proper air ventilation, the air inside your home can not only become stale, it can contain high levels of dangerous pollutants (including the growth of mold and mildew). Poor air quality can lead to a number of dangerous issues, including but not limited to:
Allergies
Asthma
Eye and nose irritation
Breathing problems
By filtering and cycling air, your home’s ventilation can not only prevent the accumulation of dangerous pollutants, but can benefit your family’s overall health and well-being.

Climate Control
A quality HVAC system will ensure that your home is not too hot when it’s warm, and not too cool when it’s cold. Your HVAC system can be programmed to set the perfect temperature year-round. By regulating your home’s temperature, it eliminates the need to run an air conditioner or heater when not necessary.

Comfort
An obvious benefit of a quality HVAC system is the overall comfort it can provide for sleeping, working and everyday living. Poor air quality can have a significant impact on your family’s overall comfort. Proper ventilation and good air quality can literally improve your family’s quality of life

Energy Efficiency
Contrary to popular belief, modern HVAC systems are an energy efficient way to control the climate inside your home. A quality HVAC system equipped with modern technology will reduce energy usage, and as a result, lower your monthly utility bill.

Health and Well-Being
A quality HVAC system can prevent VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) which are dangerous chemicals that infiltrate the air inside your home. This can benefit allergy sufferers and those with a respiratory disease.
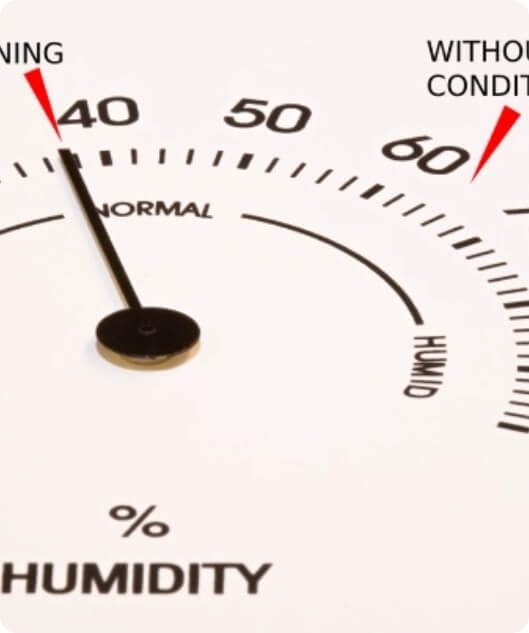

Reduce Indoor Humidity
The level of humidity in the air is an important component of indoor comfort. A quality HVAC system will help prevent excessive humidity levels by continually cycling fresh air to ensure there is enough oxygen. High indoor humidity can lead to a host of issues, including:
Respiratory infections
Growth of mold/mildew
Pest infestation (many insects, such as mites, thrive in humid environments)
Damage to paint/wallpaper
Rotting wood

ROI
With proper care and maintenance, your HVAC system should last many years. And, since modern HVAC systems offer superior energy efficiency, it will save you money on your monthly utility bills. In addition, a quality HVAC system can increase the value of your home, making it a worthy investment.

Smart Technology
Modern HVAC technology is constantly evolving. Some manufacturers now offer smart thermostats and zoning systems which enable you to create specific climate zones that are designed to enhance your home’s indoor air quality.
HVAC Terminology
As a homeowner, it’s important to understand the terms used when describing your home’s components. The following list contains the most common terminology used for HVAC systems.

AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency)
Measures a furnace’s efficiency in converting heat to energy.
Air Ducts
Air ducts (ductwork) is essentially a system of tubes that run throughout a home’s walls and ceilings. The ducts carry cool or warm air from the central HVAC unit to the various rooms in the home.
Air Handler/Exchanger
The indoor portion of a central HVAC system that enables conditioned air to flow throughout a home. The air handler/exchanger works with a heat pump to circulate warm or cool air throughout a home by converting liquid refrigerant into a gas and then back into a liquid. An air exchanger provides ventilation by allowing fresh air to flow in and vents stale air outside.
Blower
Air conditioners (including window air conditioning units) and forced air furnaces contain a blower motor (fan) that circulates air through a home’s ducts or directly into a space.
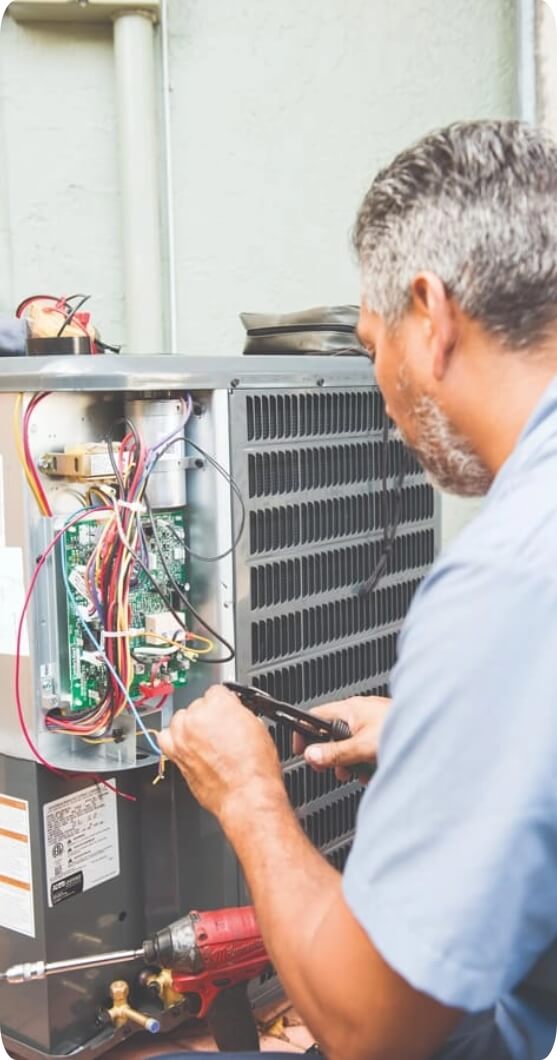

Compressor
The compressor prepares the refrigerant in order to expel heated air from the home and allow cool air to flow inside.
Condenser/Outdoor Condenser
The condenser is the outdoor component of a central air conditioning system. It plays a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle by releasing the heat the refrigerant has absorbed inside the home to the outside environment. It achieves this through coils that expel heat from the refrigerant into the ambient air. During this process, the gaseous refrigerant is pressurized and converted back into a liquid form. The outdoor condenser unit typically contains the compressor, fan motor, and refrigerant components. While a condenser provides cooling properties only, necessitating a separate heat source like a furnace, a heat pump can offer both heating and cooling by transferring warm air from outside to inside or vice versa.
Dehumidifier
A device that removes moisture from the air.
Ductless Mini-Split
Ductless mini-split systems work like a traditional split system, but without the need for ductwork and are typically mounted to walls or recessed in the ceilings. The indoor air handlers control the temperature in each space, which makes it a good option for anyone wanting to cool or heat specific rooms.

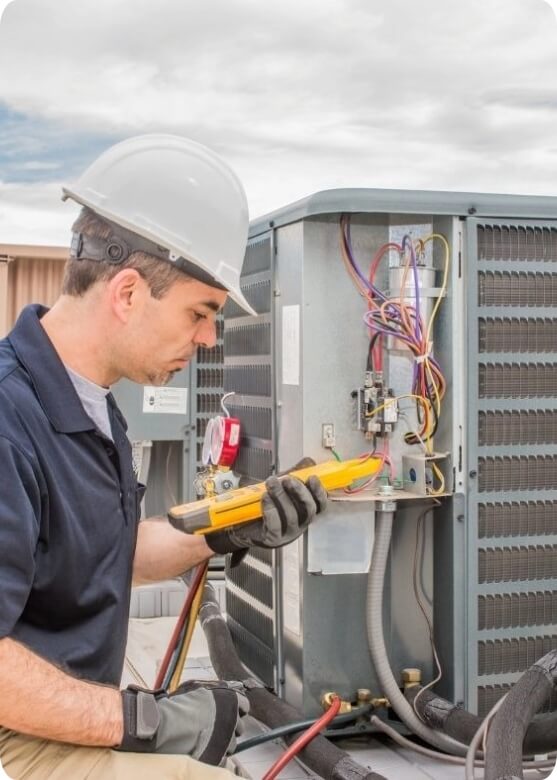
Evaporator Coils
The purpose of an evaporator coil is to cool refrigerant in order for it to effectively cool your home. Evaporator coils convert liquid refrigerant into gas. As liquid refrigerant flows through the evaporator coils it draws heat and moisture from the air and cool air is able to flow into the home.
Filter
The filter removes dust, allergens or other particles as air flows through the HVAC unit.
HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor)
The ratio for a heat pump’s heating efficiency.
Humidifier
A unit used to add moisture into the air.

Hybrid System
A dual fuel system that combines an electric heat pump with a gas furnace.
Packaged System
An all-in-one heating and/or cooling system.
Plenums
Plenums connect the ductwork to the individual heating and cooling units. There are typically two types of plenums in an HVAC system:
- Supply Plenum: Handles outflow
- Return Plenum: Handles inflow
Refrigerant (Coolant)
A liquid used to transfer heat or cool air from one place to another. Refrigerants are used in both air conditioning units and heat pumps to transfer heat either inside or outside a home. The refrigerant works with the indoor air handler to enable the flow of cool air into the home.

SEER2
Measures an air conditioner or heat pump’s cooling efficiency.
Split System
The most common type of HVAC system, a traditional split system is a great option for most homes. A split system refers to a cooling and heating solution that consists of an outdoor condenser unit and an indoor air handler that work together to provide heat in the winter and cool air in the summer.
Thermostat
A thermostat enables you to adjust your home’s temperature that can be programmed when to start and when to stop using digital, analog (traditional) or smart technology. Smart thermostats integrate with a home’s smart systems and can “learn” over time the most energy efficient way to cool or heat your home. In addition, smart technology allows you to control the thermostat from anywhere in the world.
Vents
Vents connect the ductwork to a home’s interior to ensure proper airflow and fresh air.
Considerations
Before investing in a new HVAC system for your home, there are several things to consider. There are multiple factors that can impact the effectiveness of your HVAC system.

Age of Home
Most newer homes are built to provide energy efficiency and are tightly sealed to ensure air is not able to leak from windows and doors. As a result, natural ventilation is impossible and requires mechanical ventilation via an HVAC system.
Air Ducts (Ductwork)
If you are considering investing in a new HVAC system, it’s important to ensure that your existing duct system is compatible.
Climate
Regional temperature fluctuations are also an important factor in the type of HVAC system to choose. Depending on where you live, the local climate will dictate what system would be most efficient for your needs.
Doors and Windows
If the doors and windows in your home were not installed properly or haven’t been regularly maintained, the seals can become compressed, causing air to leak in and out of your home. These leaks will not only make your HVAC system work harder, they will also increase your home’s energy usage.

Furnaces
Because furnaces typically run on natural gas, propane or heating oil, they can produce toxic fumes, such as carbon monoxide. If not properly ventilated, the fumes can become a very serious safety hazard.
Installation
Proper installation is a critical component of an effective HVAC system. Improperly installed systems often result in expensive repairs and uncomfortable living conditions. In addition, shoddy installation can have a direct impact on your home’s energy efficiency.
Insulation
If your home is not insulated properly, your HVAC system will not be able to function efficiently.
Maintenance
Preventative maintenance and maintaining your product’s warranties are the best ways to ensure your home’s HVAC system is performing at its optimal level. Routine maintenance on your HVAC system can not only extend its life, but can detect issues before they become expensive repairs. HVAC system maintenance includes, but is not limited to:
- Ensuring all parts are in good working order.
- Replacing worn/faulty parts.
- Inspecting the heat exchanger and heating elements.
- Cleaning condensers and coils.
- Detecting leaks.
- Replacing filters.
- Inspecting ducts for debris, mold/mildew, etc.
We recommend the following standards for scheduling HVAC maintenance:
- Late Summer/Early Fall: Heating system (heat pump or furnace) inspection before you need heat.
- Late Winter/Early Spring: Cooling system inspection (air conditioning or heat pump) before you need to cool your home.
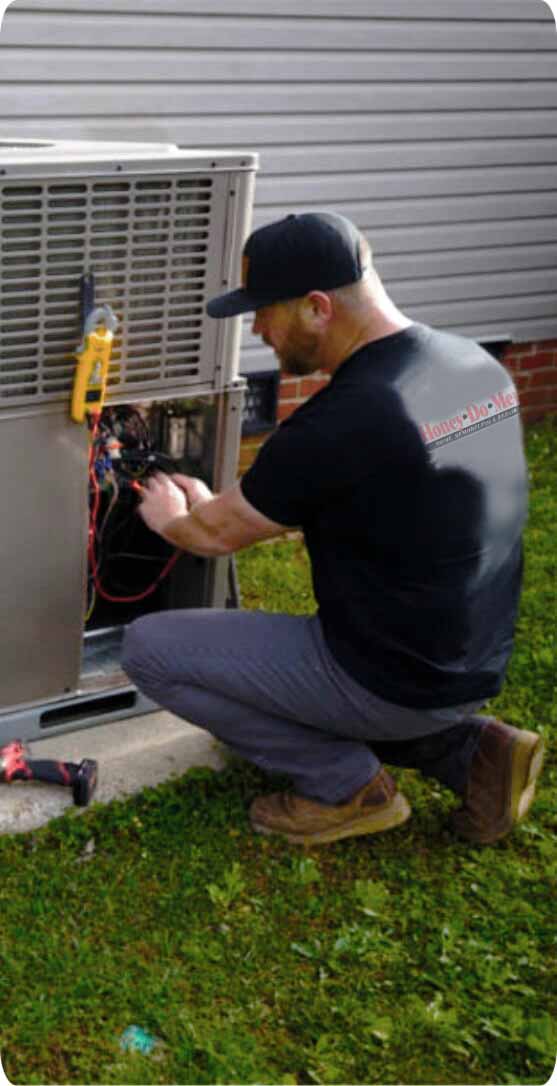

Refrigerant/Coolant
In the past, Freon was the primary form of coolant. However, modern units use something called Puron, which is more environmentally safe. Older air conditioning units will require Freon, so if you are looking for something that is safe for the environment, you’ll need to invest in a new unit. As of January 2020, Freon is no longer available in the U.S. If you have an older unit, you’ll need to switch to a modern unit when the Freon is depleted.
Replacement
An improperly working HVAC system is the first indication it needs to be repaired or replaced. If you notice that your system isn’t maintaining a comfortable temperature and/or your home’s energy usage has increased, contact an HVAC professional such as Honey Do Men to assess your system and make recommendations.
Size of Home
The size of your home will dictate the type of HVAC system that would work best for your home.
Thermostats
For optimal performance and functionality, it's crucial to select a thermostat that's compatible with your HVAC system. While many manufacturers design thermostats to work seamlessly with their HVAC units, using an incompatible thermostat can prevent the system from operating correctly.
Choosing the Right HVAC Professional
When it comes to HVAC systems, it’s very important to choose a qualified professional. HVAC is a highly specialized field and requires specialized knowledge, expertise and tools. In most cases, HVAC system installation should be left to experts, such as Honey Do Men.
Every HVAC professional should possess an up-to-date license specifically for HVAC system installation and repair. Regular training is essential to keep abreast of advancements in HVAC technology. Furthermore, for optimal functionality and efficiency, HVAC system components must be correctly installed and consistently maintained.
At Honey Do Men, our team of HVAC professionals are trained and certified to offer the highest quality HVAC services, maintenance, repair and installation. Call us today and schedule a complimentary assessment so we can ensure that your home stays comfortable all year long.
TESTIMONIALWhat Our Customers Say About Us
Common HVAC Systems Questions
It's generally recommended to change your HVAC air filter every 1-3 months, depending on usage and the type of filter. If you have pets or allergies, consider changing it more frequently to ensure optimal air quality.
To Schedule A Complimentary Consultation With One Of Our Specialists
Give us a call today.
Contact us
